BLOG
DELCO Valve Provide Various Optimal Solution For Industrial Valves, Especially For Control Valves.
TAGS
Contact Us
What is a Manual Globe Valve?
- Morning Jiang
A manual globe valve is a type of linear motion valve used to regulate fluid flow. It features a spherical valve body and a disc that moves perpendicular to the flow path, which is the origin of its name. By simply rotating the handwheel, the fluid flow rate can be adjusted to the desired level. Due to its precise flow control and straightforward operation and maintenance, the manual globe valve is widely used in various industrial applications. Common applications include water treatment, oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation. This article will explore the design, function, applications, advantages, and maintenance considerations of manual globe valves in detail.
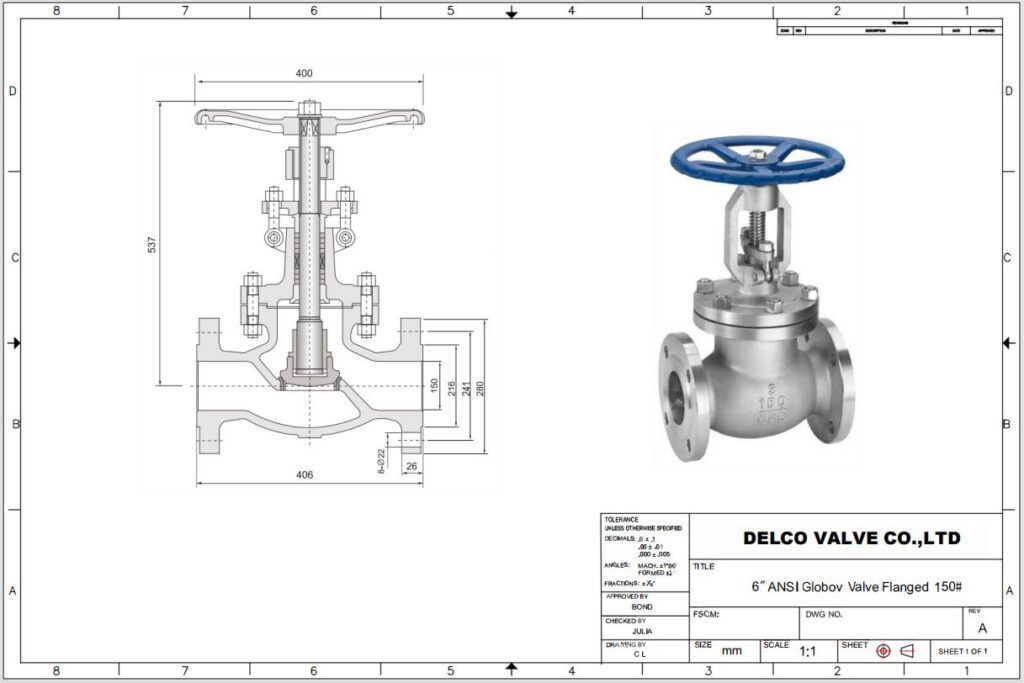
Structure of a Globe Valve
A manual globe valve is composed of several key components, including the valve body, bonnet, stem, disc, seat, and handwheel:
– Valve Body: Contains the internal components and connects to the pipeline. It is usually made of stainless steel, cast iron, carbon steel, or alloy materials.
– Bonnet: Located at the top of the valve, acting as a cover that seals the internal parts of the valve.
– Stem: A threaded shaft that connects the handwheel and the disc. When the handwheel is turned, the stem moves the disc up and down, controlling the flow of fluid through the valve.
– Disc: A movable element used to throttle or stop the flow.
– Seat: The fixed part where the disc seals. This design allows precise control of fluid flow, making globe valves ideal for regulating flow.
– Handwheel or Actuator: The manual or automatic mechanism for operating the valve.
There are several types of globe valves, each suitable for specific applications and operational requirements. The three main types are:
– Z-Type Globe Valve (Straight-Through Globe Valve): The most common type, featuring a Z-shaped diaphragm. The horizontal seat allows the stem and disc to move perpendicular to the flow direction. This design provides a simplified flow path, reducing turbulence and pressure drop.
– Y-Type Globe Valve: These valves have a Y-shaped body, with the stem and seat arranged at an angle. The inlet and outlet of the Y-type valve are at a 45-degree angle, reducing flow resistance and pressure drop, making them suitable for applications requiring high flow and low-pressure drop.
– Angle Globe Valve: The valve body has a 90-degree turn, combining the functions of a globe valve and a pipe elbow, reducing the number of fittings required. This type is suitable for applications needing a change in flow direction or where space is limited.
Functions of Globe Valves
The primary functions of manual globe valves include:
- Flow Control: By adjusting the handwheel, the disc moves up and down within the valve body, changing the opening of the fluid passage. This design allows the operator to precisely regulate the fluid flow, from fully closed to fully open, and any intermediate position.
- Shutoff and On-Off Control: Manual globe valves can be used to completely shut off or open the fluid flow. When the disc is fully pressed against the seat, fluid flow stops completely; when the disc is fully lifted, fluid can flow freely.
- Precise Regulation: Manual globe valves can precisely regulate fluid flow at different openings, suitable for applications requiring accurate adjustment.
- Pressure Regulation: Manual globe valves can also be used to regulate system pressure. By partially opening or closing the valve, the fluid resistance can be increased or decreased, thereby adjusting downstream pressure.
- Preventing Backflow: When the system is shut down, closing the valve can prevent fluid backflow, protecting the system and equipment from damage.
- Flow Direction Control: Manual globe valves can be installed in piping systems requiring a change in fluid flow direction, especially angle globe valves.
- Emergency Shutoff: In emergencies, manual globe valves can be quickly closed, ensuring the safety of the system and operators.
Advantages
Manual globe valves have several advantages, making them a preferred choice in many industrial applications:
- Precise Throttling: The design allows precise flow control, ideal for applications requiring fine adjustments.
- Reliable Sealing: The vertical movement of the disc ensures a tight seal against the seat, minimizing leakage when the valve is closed.
- Durability: Made from robust materials, globe valves can withstand harsh operating conditions such as high temperatures and pressures and prolonged use.
- Versatility: Available in various sizes, materials, and configurations, globe valves can be customized to meet specific application requirements.
- Ease of Maintenance: The straightforward design allows for easy disassembly and maintenance, reducing downtime and operating costs.
Maintenance Considerations
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and performance of manual globe valves. Key maintenance practices include:
- Regular Inspection: Regularly checking for signs of wear, corrosion, and leakage helps identify potential problems and address them promptly.
- Lubrication: Keeping the stem and other moving parts well-lubricated ensures smooth operation and prevents sticking.
- Cleaning: Removing debris and buildup from valve components prevents blockages and maintains optimal performance.
- Replacing Worn Parts: Timely replacement of worn or damaged parts such as discs, seats, and stems prevents leakage and ensures reliable operation.
- Proper Installation: Ensuring proper installation, including correct alignment, secure fixing, and proper orientation of the disc, minimizes stress and wear on components.
Conclusion
Manual globe valves are essential components in fluid control systems, offering precise flow regulation, reliable sealing, and robust construction. Their versatility and adaptability make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, from water treatment and chemical processing to oil and gas and power generation. By understanding their design, functions, and maintenance requirements, operators can maximize the performance and lifespan of these critical valves, ensuring efficient and safe operation of fluid systems.