เราไม่เพียงแต่ให้ใบเสนอราคาแบบง่าย ๆ แต่เรายังเป็นผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านการคัดเลือก การคำนวณ และการวาดภาพอีกด้วย
ข้อมูลการติดต่อ
- +86 -1598-9602972
- สอบถามข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่@delcofluid.com
- ถนนหว่านเจียง เมืองตงกวน ประเทศจีน
ตัวเลือกยอดนิยม
-
DELCO DK07 Pilot Operated Diaphragm Type Stainless Steel Solenoid Valve
โซลินอยด์วาล์วควบคุมด้วยนักบิน อ่านเพิ่ม
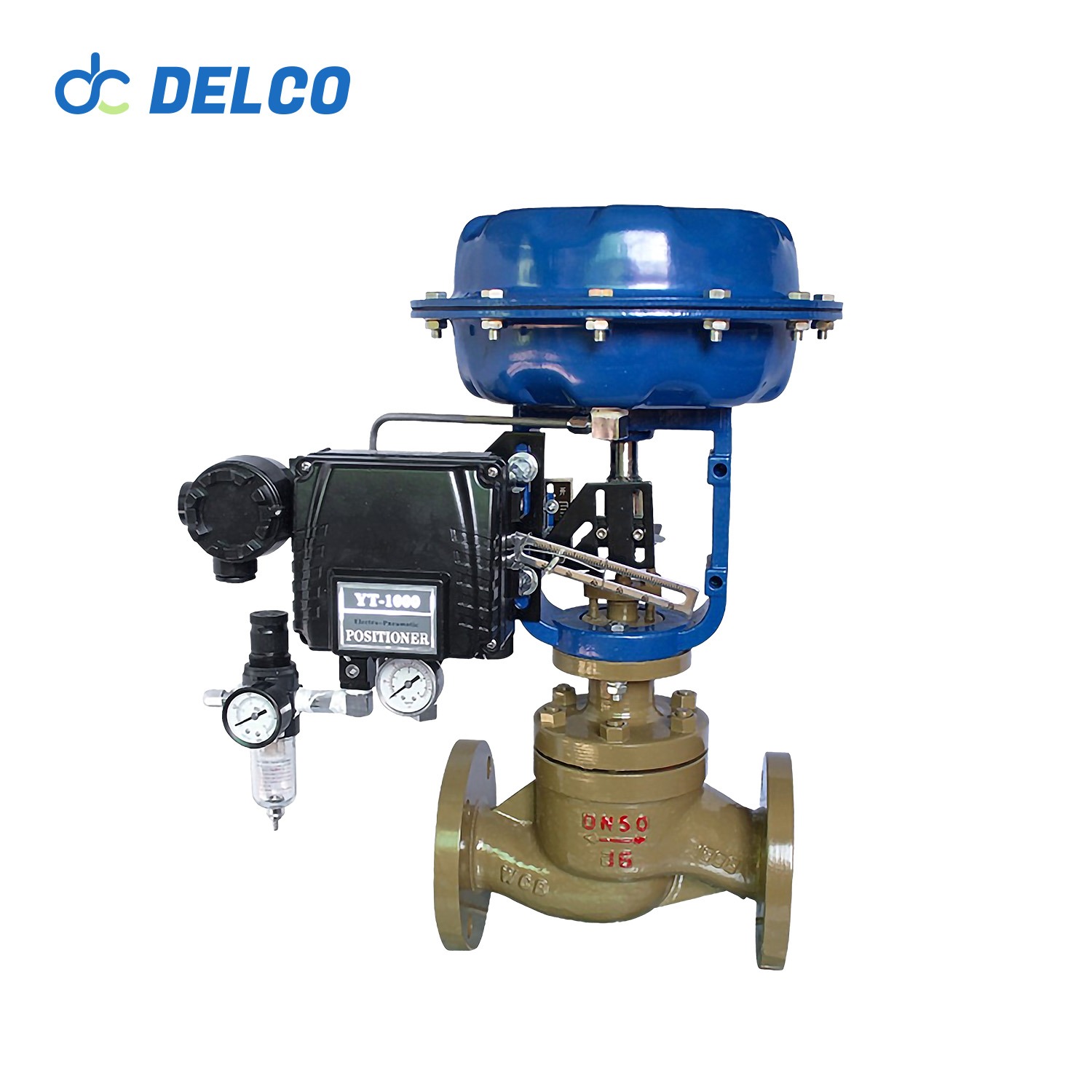
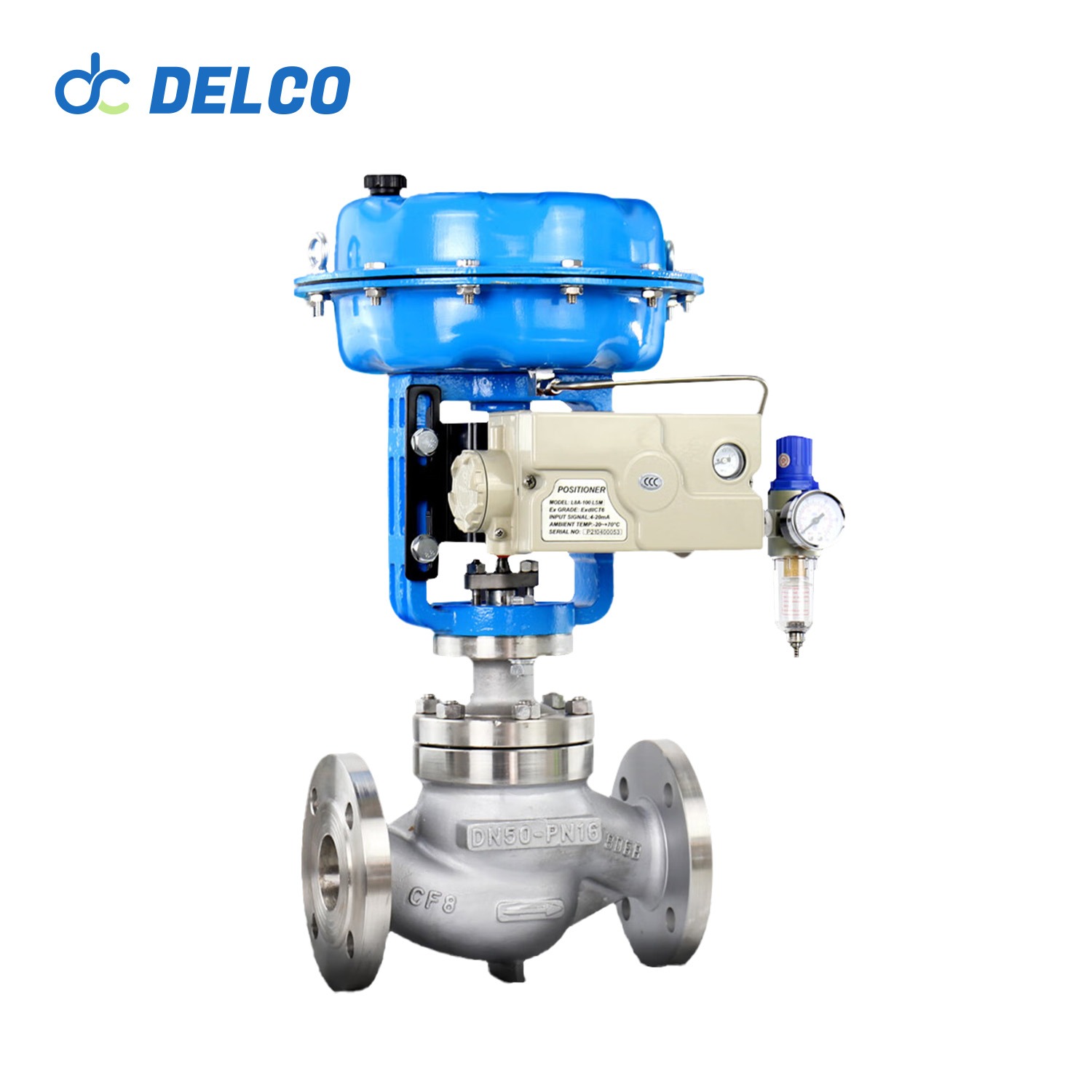
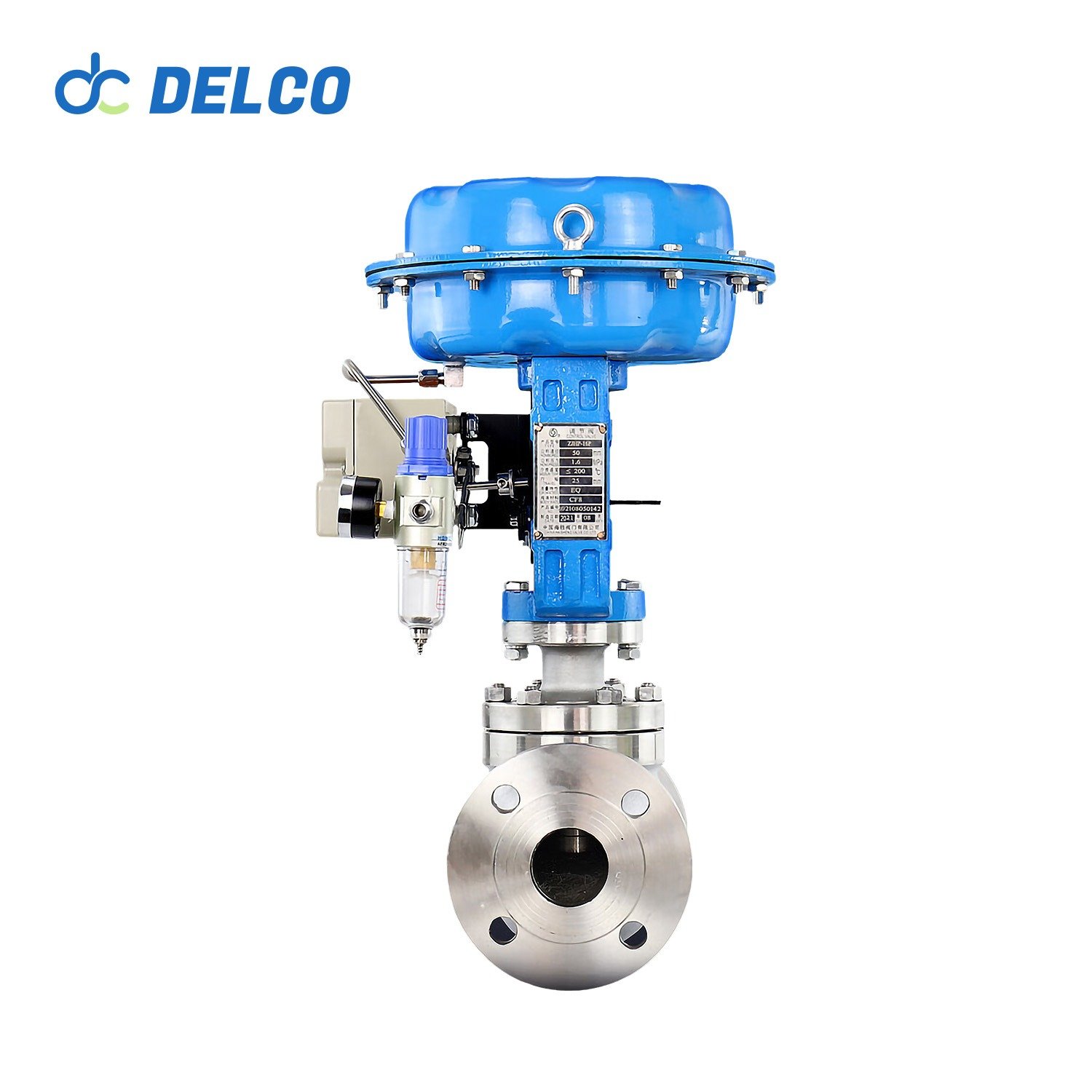
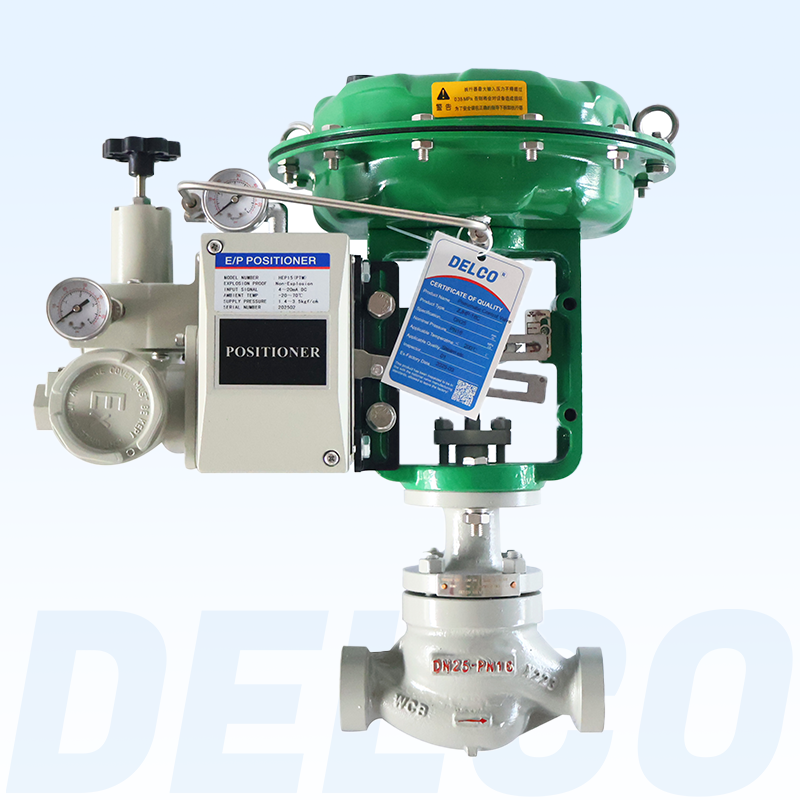
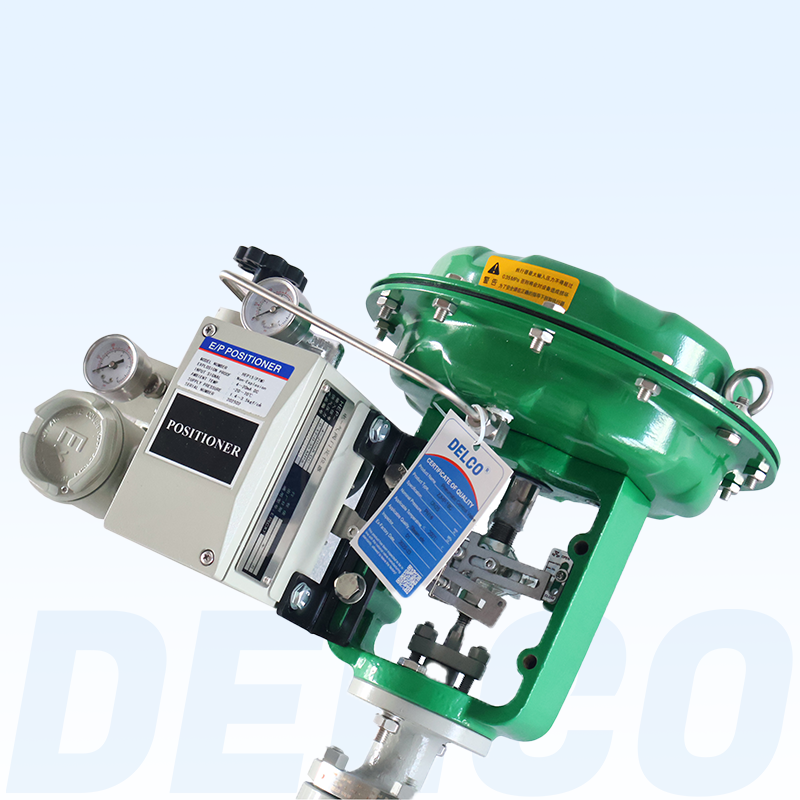
DELCO Valve Single Seat Pneumatic Control Valves
It has a low center of gravity, high vibration resistance, and is easy to install.
These are extensively utilized in automated production control systems across various industries such as chemistry, petroleum, light industry, power stations, and metallurgy.
DELCO Valve is dedicated to offering our customers top-quality products at the most competitive prices, ensuring timely delivery and comprehensive warranty service.
แบบอย่าง: ZJHP/ZJHM
ช่วงขนาด: 1/2”~12′
ช่วงความดัน: 1.6~6.4Mpa
วัสดุ: WCB, Stainless Steel 304, 316, 316L
รับใบเสนอราคาทันที
ซัพพลายเออร์ที่ดีไม่เพียงแต่ทำให้คุณหมดกังวลเท่านั้น แต่ยังช่วยให้ธุรกิจของคุณพัฒนาอย่างยั่งยืนและทำให้แบรนด์ของคุณได้รับชื่อเสียงด้านการบริการและคุณภาพอย่างต่อเนื่องอีกด้วย
Introduction to Pneumatic Control Valves:
Pneumatic control valves operate using compressed gas as their power source, utilizing a cylinder as the actuator. With the assistance of various components such as valve positioners, converters, solenoid valves, check valves, gas tanks, and gas filters, these valves are driven to achieve on/off functions or proportional adjustments. They receive control signals from industrial automation systems to regulate various process parameters in pipelines, including flow, pressure, temperature, and liquid level. Pneumatic control valves are characterized by their straightforward control, quick response, and inherent safety, eliminating the need for additional explosion-proof measures.
The primary benefits of pneumatic control valves include the ease of adjusting their opening and closing speeds, their simple structure, and ease of maintenance. Thanks to the natural cushioning properties of gas, they are less prone to damage from jamming during operation. In certain explosion-proof scenarios, they offer greater reliability compared to electric valves.
Introduction to Pneumatic Control Valves:
| พิมพ์ | แรงดันที่กำหนด | โครงสร้าง | Cooling type | Packing |
| Single-seat, double-seat, sleeve | PN16, PN25, PN40, PN64 | Standard type (-20℃ ~+200℃ ) |
(-40~450℃ ) | V type PTFE, flexible graphite |
| เส้นผ่านศูนย์กลางที่กำหนด | การเชื่อมต่อ | วัสดุ | Low-temperature type | Adjustable range |
| DN15-DN300 | Flange, thread, weld (Or other customer specified) |
WCB, 304, 316, 316L | (-60℃ ~-196℃ ) | 50:1 |
| Sealing surface | Basic error | Accessories | Leakage class | |
| PN16 convex surface, PN40, PN63, PN100 | Less than full stroke +-1% (With locator) Less than full | locator, air filter pressure-relief valve, hand wheel device, limit switch, solenoid valve, lock up valve, and others. | Metal seal: Less than 0.01 (ANSI B16.104-1976IV) | Soft seal: Less than 0.00001% |
Valve Components: Features a single-seat plunger core design with a 304 or 316+ SLT core seat, offering equal percentage, linear, and quick-opening flow characteristics.
Valve Actuator: Utilizes a multi-spring diaphragm actuator available in both direct and reverse actions. The diaphragm is made from NBR rubber reinforced with polyester fabric. The spring ranges include 20-100 KPa, 40-200 KPa, and 80-240 KPa, with supply pressures ranging from 0.4 MPa to 0.5 MPa.
Action Type: For air-to-close (FO) operation with a direct action actuator, the actuator spring opens the valve when the air supply fails. For air-to-open (FC) operation with a reverse action actuator, the actuator spring closes the valve when the air supply fails. Provides linear, equal percentage, and quick-opening characteristics.
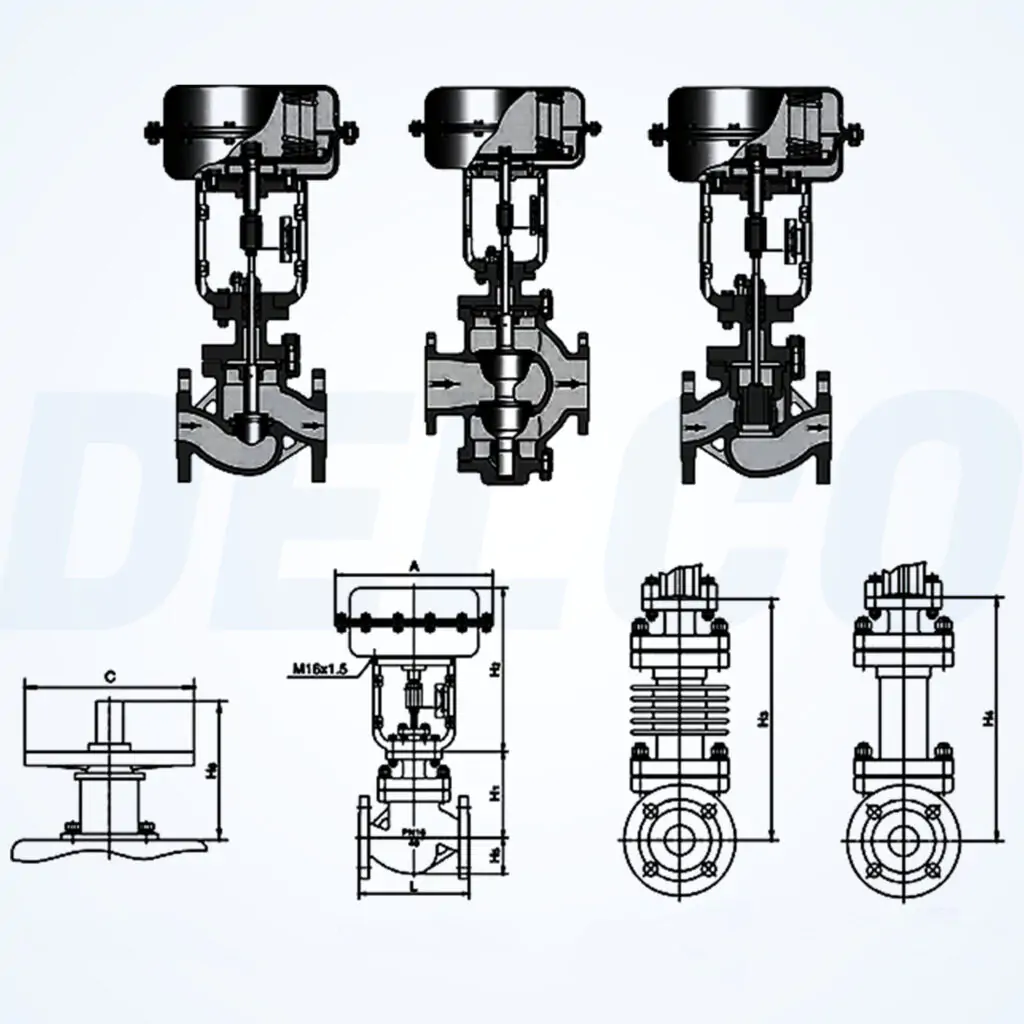
When selecting a control valve, consider the following factors:
Flow requirements: Evaluate the flow characteristics needed for the specific application.
Flow Characteristics: Consider the fluid’s properties, such as viscosity, pressure, and temperature, to select a valve that can handle the specific conditions.
Valve size: Choose a valve size that matches the pipeline size and meets the required flow capacity.
Actuator type: Decide between manual, electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuation based on the system requirements and available resources. Select an actuator that provides adequate force and meets the desired control requirements.
Material compatibility: Ensure the valve materials are compatible with the fluid being handled to avoid corrosion or other damage.
Regulatory requirements: Adhere to industry-specific regulations and standards to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Noise and vibration: Option for a valve design that minimizes noise and vibration for a safer, more reliable operation.




รับใบเสนอราคาอย่างรวดเร็ว
แนะนำ
-
DELCO DK07 Pilot Operated Diaphragm Type Stainless Steel Solenoid Valve
โซลินอยด์วาล์วควบคุมด้วยนักบิน อ่านเพิ่ม

รับใบเสนอราคาอย่างรวดเร็ว
แนะนำ
-
DELCO DK07 Pilot Operated Diaphragm Type Stainless Steel Solenoid Valve
โซลินอยด์วาล์วควบคุมด้วยนักบิน อ่านเพิ่ม









